Section 1. Topics on theoretical electrodynamics
BREWSTER-LIKE REFLECTIONLESS TRANSMISSION OF EVANESCENT WAVES THROUGH A PLANE TWO-MEDIA INTERFACE
Ignatov A.I., Merzlikin A.M.
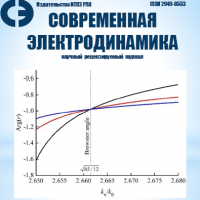
We propose a Brewster-like reflectionless transmission effect of evanescent waves: no evanescent reflected waves are observed at evanescent wave incidence on a plane interface of two media. Similar to the well-known Brewster effect for propagating waves, the proposed Brewster-like effect for evanescent waves occurs when surface impedances of waves in the neighboring media are equal. Contrary to the known Brewster effect for complex incidence angles related to the existence of some surface wave (when surface impedances are equal for evanescent waves to both sides of the two-media interface decaying in the directions away from the interface), the proposed Brewster-like reflectionless transmission corresponds to the surface impedances equality for evanescent waves decaying in the same direction. It was shown that the proposed Brewster-like effect for evanescent waves can occur for both (p- and s-) polarizations and only for magnetic media (µ/=1 for at least one of the two neighboring media). Based on the proposed Brewster-like reflectionless transmission of evanescent waves, we suggest a method of a totally-reflected-wave’s phase patterning with a pattern vanishing exactly at Brewster’s angle.
Keywords: Brewster effect, evanescent wave, near field, magnetodielectric, surface wave
Section 2. Topics on experimental electrodynamics
MODERNIZATION OF THE SERRATED EDGE OF THE MARK-12 COLLIMATOR
Balabukha N. P., Zubov A. S., Menshikh N. L., Solosin V. S.
The problem of optimizing the serrated edge of the collimator MARK-12 is considered. The serrated or rolled edge of the mirror is used to reduce the influence of diffraction effects on the field distribution in the quiet zone of the collimator. Currently, teeth with curved edges have been widely introduced, which, at the same height, provide a more uniform distribution of the field in the quiet zone of a compact ranges. Using model of the two-dimensional collimator, the shape of the tooth profile was found by iteration, which provides the best smoothness of the field distribution in the quiet zone. The calculation of the diffraction problem was performed by the method of integral equations. It was shown that the field distributions in the model problem strongly depend on the polarization of the incident wave for both serrations with rectilinear and curved edges. Then a number of options for the arrangement of serrations with an optimized shape of the edges on the edge of the parabolic part of the collimator MARK-12 were considered. The physical optics method was used to evaluate the distribution of fields in the quiet zone of the collimator. It was shown that the modification of the shape of the serrated edge will reduce the nonuniformity of the field distribution in the quiet zone of the collimator by 0.6 dB in the low-frequency part of the range while maintaining the overall dimensions of the mirror.
Key words: compact range, reflector, quiet zone, field distribution, serrated edge
Section 3. Topics on interaction of an electromagnetic field with materials
MODEL OF ERBIUM FIBER AMPLIFIER FOR AN ANALYSIS OF PROPAGATION OF SIGNAL AND NOISE
Dorofeenko A. V., Nechepurenko I. A., Bazakutsa A. P., Butov O. V.
A model of an erbium fiber amplifier is proposed that takes into account main processes of spontaneous and induced emission. A nonuniform pump power, signal, and noise distribution along the fiber is taken into account. An estimate is made of the magnitude of spontaneous emission noise.
Key words: fiber amplifiers, erbium amplifiers, three-level system, rate equations
Section 4. Metodological notes
Andrianov E. S., Vinogradov A. P.
The algorithm of local plasmon quantization is discussed.
Key words: plasmon, quantization of quasi-static fields

Editorial address: 13 b. 6, Izhorskaya st.,
This site respects your rights and maintains confidentiality when filling out, transmitting and storing your confidential information.
Placing an application on this site means your consent to the processing of data and the further transfer of your contact information to our company.
Personal data means information related to the subject of personal data, in particular the name, contact details (email address) and other data classified as personal data by Federal Law of July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ “On Personal Data.”
The purpose of processing personal data is to inform about the services provided by our company.
